As part of our efforts to build optimized, intuitive keyboard layouts for Indian languages, we’ve conducted detailed character frequency analysis for Malayalam. This post presents our findings—showing which characters, vowels, and consonants occur most frequently in real-world usage based on large Malayalam dataset—and briefly discusses how this data influenced the keyboard design.
For an explanation of our overall keyboard design methodology, including the rationale behind layout decisions, please refer to our Tamil keyboard design post: Designing a New Input Method for Tamil
Dataset Used for Frequency Analysis
To ensure broad linguistic coverage and reliability, we used Malayalam corpora by combining text data from multiple sources, including:
- IndicCorp
- Swathantra Malayalam corpus
- Wikipedia Malayalam corpus
- News articles, blogs, etc.
Here is the high-level statistics of the corpora used in our analysis:
- Total words: 1.699 billion
- Unique words: 25.345 million
This large and diverse dataset gives us a realistic view of character usage in modern written Malayalam.
Overall Character Frequency Heatmap
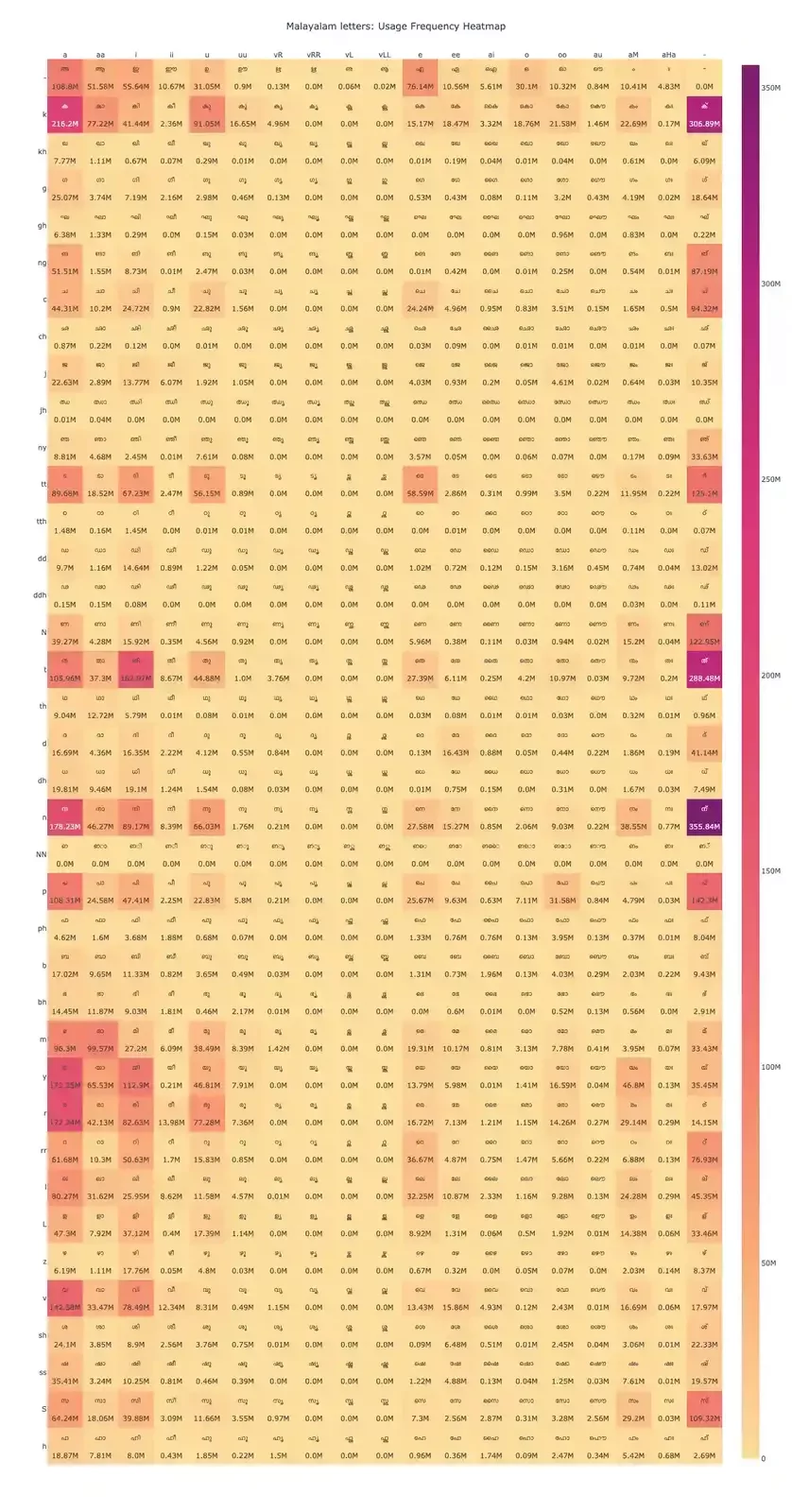
Characters such as അ (a), മ (ma), ന (na), and ക (ka) appear with consistently dark shades, across their rows, indicating they are among the most frequently used. These are foundational phonemes in Malayalam and are common across both spoken and written forms. Characters like പ (pa), ത (tha), and ല (la) show moderate frequency across their respective row, suggesting they are contextually important but not as dominant. Their usage may vary depending on the domain (e.g., literary vs. conversational text).
Vowel Frequency Heatmap
To gain deeper insights, we examined the frequency of Malayalam vowels both in their standalone and combined consonant-vowel forms. This analysis was derived by summing the columns of our overall character frequency chart, offering a clear view of vowel usage patterns. The results are visualized in the chart below.
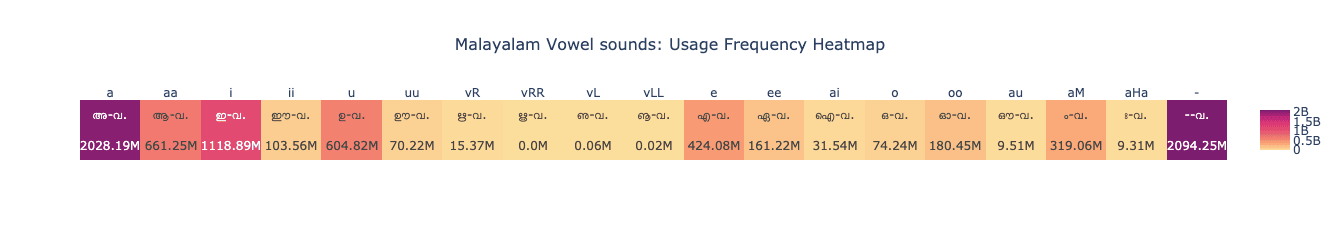
Malayalam has a rich vowel system, but a handful of vowels—especially അ, ഇ, ഉ, and എ—occur most frequently. Further as expected, the shorter vowels are more frequent than their longer versions. Note that these counts include the usage frequency of vowels as well as the vowel sign glyphs in their consonant vowel forms. The last cell in the heat map actually refers to the frequency of the Chandrakala (Virama) character.
Consonant Frequency Heatmap
In addition to vowels, we also analyzed the frequency of Malayalam consonants. This was done by summing the rows of the overall character frequency chart, which highlights how often each consonant appears across different vowel combinations. The resulting data provides a clearer picture of consonant usage patterns in the language.

Among consonants, we can see a clear dominance of ക്, ന്, ത് യ്, and ര്. These findings informed our decisions in distributing consonants across the keyboard layout for minimizing the finger movements during typing. In line with the InScript keyboard layout convention, each aspirated consonant was assigned to a specific key, while its corresponding unaspirated counterpart was placed in the corresponding shift position.
Chillaksharam Frequency Heatmap
We also analyzed the frequency of chillaksharam (ചില്ലക്ഷരം)—the special consonant forms used at the end of syllables in Malayalam, such as ൽ, ൻ, ൾ, and ൿ. These characters are essential for accurate representation of the language and are frequently used in written text.
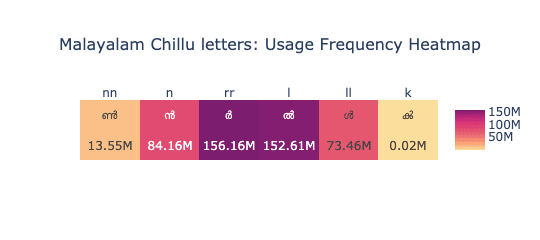
Following our keyboard design principles, each chillaksharam is placed in the Alt + Shift position of the corresponding base consonant key. For example, the character ൿ is mapped to the Alt + Shift position of the ക് key. Since mobile keyboards typically do not include an Alt key, these chillaksharam characters are made accessible through long-press gestures on their respective base keys. So, long-pressing the ക് key on a mobile keyboard would reveal ൿ, ensuring consistency and ease of access across platforms.
Impact on Keyboard Layout Design
Whether you're using a Malayalam phonetic keyboard or a standard Malayalam keyboard, these insights can guide better input method development. As part of our design, we excluded individual vowel signs and instead generate them dynamically from consonant-vowel combinations. This approach reduces complexity and prevents invalid character sequences.
These frequency trends helps in designing the layout for our Malayalam keyboard. High-frequency characters were assigned to primary home row or easy index finger positions, ensuring reduced typing effort and faster input for users. Low-frequency characters were positioned in secondary or long-press locations. As part of our design, we excluded individual vowel signs and instead generate them dynamically from consonant-vowel combinations. This approach reduces complexity and prevents invalid character sequences.
You can explore our optimized keyboard layout through the Varta Keyboard apps, available on Android and iOS, as well as through browser extensions for Chrome, Edge, and Safari.
Explore Frequency Analyses in Other Languages
We’ve performed similar analysis for other Indian languages as well. Explore them below:
